How Fake Fingerprint Detection Works?

As we navigate a more digital world, secure authentication methods are vital. With the rise in cyber threats, many now trust biometric solutions to protect sensitive data. Biometric recognition is emerging as the top choice. It is convenient, accurate, and widely accepted.
However, the very technology that offers enhanced security also presents new vulnerabilities. The emergence of fake fingerprints - artificial replicas designed to bypass the biometric systems. It poses a significant challenge to the integrity of fingerprint recognition.
These counterfeit prints can be crafted using a variety of materials and techniques, effectively mimicking the unique patterns and characteristics of genuine human fingerprints. As a result, the security biometric systems are increasingly at risk, raising alarms for both individuals and organizations that rely on these technologies for protection.
Before diving into the Fake Fingerprints, let’s take an overview of fingerprint authentication.
Biometric Fingerprint Authentication - An overview
Fingerprint authentication is a safe way to verify the identity of an ndividual without traditional authentication approaches such as passwords and PINs. Here identity management systems are responsible for preventing identity fraud.
With the adoption of fingerprint authentication in our daily lives including but not limited to cell phones, laptops, access control, financial transactions, smart home protection, and Law enforcement, it has become a vital part. It is important to note that no fingerprint is the same, even with the twins.
Here are some examples, of the distinct fingerprints



Understanding the Threat: What are the Fake Fingerprints
Spoof fingerprints, or fake fingerprints, are synthetic copies of real fingerprints intended to trick biometric systems. These copies can be made from different materials and can imitate the distinctive patterns on human fingertips. Let’s see which materials are used in developing these fake fingerprints.
Materials used for fingerprint spoofing
Silicone
Gelatin
3D-printing materials
Other materials such as Wood, Latex, and Clay dough can also be used.
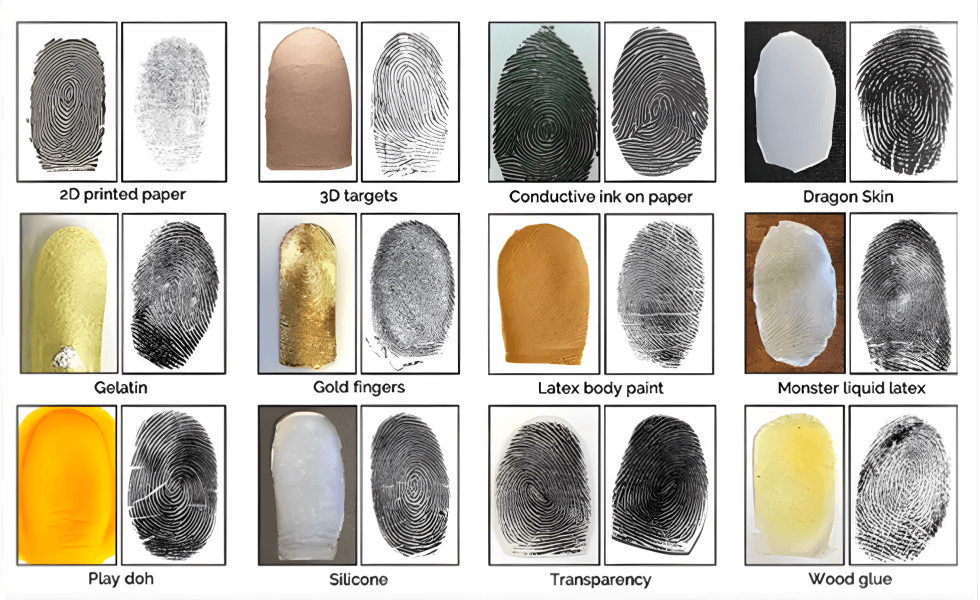
These materials can be molded to replicate the intricate details of the real fingerprint. This makes it more challenging for the standard fingerprint scanners to differentiate genuine fingerprints from fake ones.
What are the Risks Associated with Fingerprint Spoofing?
The primary reason associated with fingerprint spoofing is unauthorized access to secure systems. Criminals can exploit vulnerabilities in biometrics systems, potentially leading to data breaches and financial loss. Moreover, the growing sophistication of spoofing techniques poses a significant threat to personal and organizational security.
Understand the Science behind Fake Fingerprint Detection
The biological properties of human skin are combined with cutting-edge technical capabilities to detect forged fingerprints. It is difficult to duplicate the distinct textures, electrical conductivity, and thermal characteristics of real fingerprints in synthetic materials. These properties are analyzed by a variety of sensor technologies, such as optical, capacitive, ultrasonic, and multispectral imaging, to distinguish between authentic and fraudulent prints. But complex spoofing strategies like "DeepMasterPrints" make it harder to identify threats, emphasizing the urgent need for better ways to strengthen biometric security against changing threats. The below image shows the difference between the Live fingerprint and the Spoofed fingerprint.
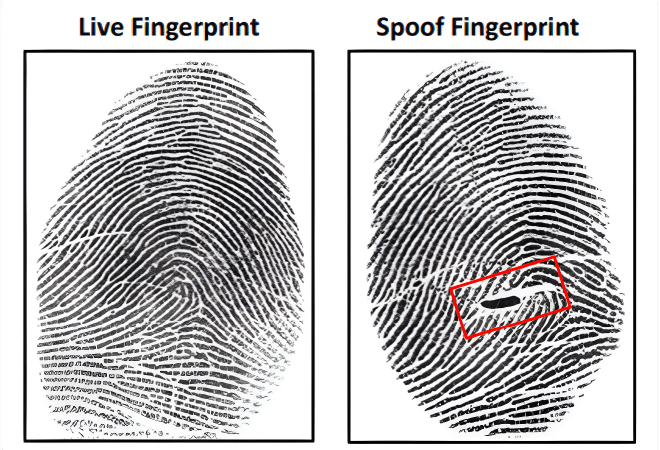
Source: Fingerprint Spoof Buster: Use of Minutiae-centered Patches Tarang Chugh*, Student Member, IEEE, Kai Cao, and Anil K. Jain, Life Fellow, IEEE
Various methods have been developed to enhance the accuracy & readability of fingerprint scanners, each one with its own set of strengths and limitations. Here is the breakdown of each of these methods.
Key Methods of Fake Fingerprint Detection
Fake fingerprint detection techniques are developing along with fingerprint recognition technologies. To guarantee that biometric systems exclusively identify real, living fingerprints, a number of strategies have been devised. The most popular techniques for detecting phony fingerprints are listed below; each has a special methodology, benefits, and drawbacks.
1. Optical Liveness Detection
Optical scanners such as Mantra Identity’s MELO31 Optical Fingerprint Scanner, are the traditional fingerprint scanners. They use a light source and photodiode to capture the digital image of the fingerprint. While it is simple to use, these scanners can be easily fooled by the high-quality replicas available. To counter this, optical liveness detection shines the light on the finger, measuring the reflection, how it is absorbed, or how it is scattered by the skin. This method identifies liveness by identifying the unique optical properties of the live skin. This helps in distinguishing genuine fingerprints from the spoofed ones.
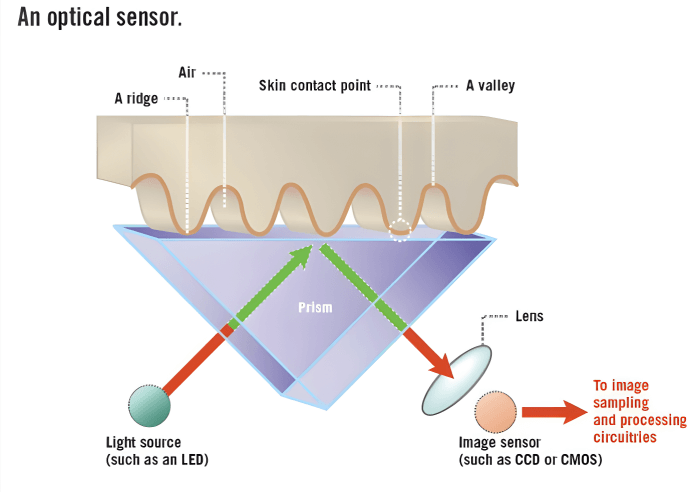
Source: androidauthority.com
Advantages
Able to take pictures with a good resolution.
Non-intrusive and simple to use.
Limitations
Sensitive to illumination and other environmental conditions.
Can be tricked by superior imitations.
2. Capacitive Liveness Detection
Capacitive scanners, widely used in smartphones, employ electrical currents to accurately map the ridges and valleys of a fingerprint, providing higher resolution and enhanced security compared to optical scanners. These scanners measure the electrical conductivity of the skin, allowing them to differentiate between real and fake fingerprints. Live human skin possesses distinct conductive properties that are not present in most spoofing materials, making capacitive scanners particularly effective at detecting and rejecting counterfeit fingerprints. This technology enhances biometric security significantly.
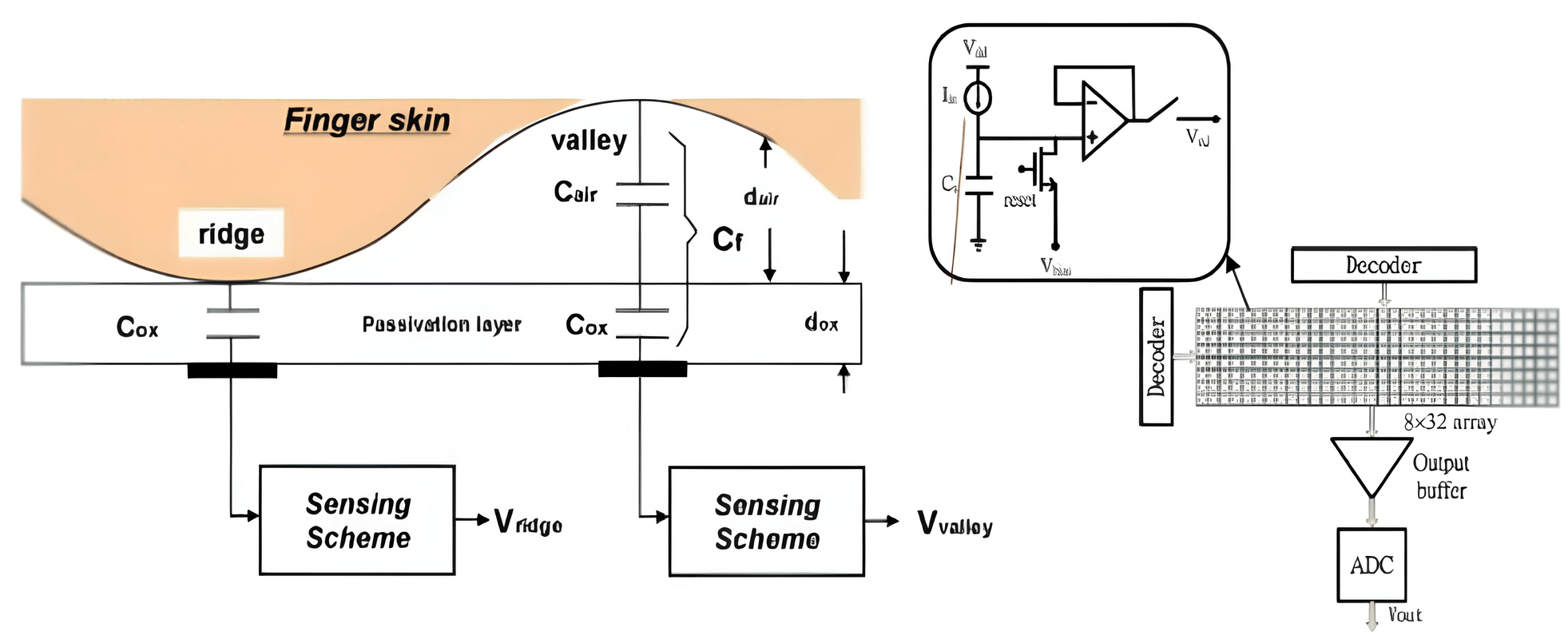
Source: androidauthority.com
Advantages
Effective against a wide range of spoofing materials.
Reliable in various environmental conditions.
Limitations
May struggle with certain materials that closely mimic human skin's electrical properties.
Higher cost compared to optical systems.
3. Thermal Liveness Detection
Thermal scanners are the least common fingerprint scanners, primarily due to their high cost and sensitivity to ambient temperature. They work by detecting heat differences on the contact surface, which allows them to identify genuine fingerprints based on the warmth of living tissue. This heat detection contrasts with the cooler temperature of fake fingerprints, making thermal scanners effective at distinguishing real fingerprints from replicas. Despite their advantages, the high cost and environmental sensitivity limit their widespread use.
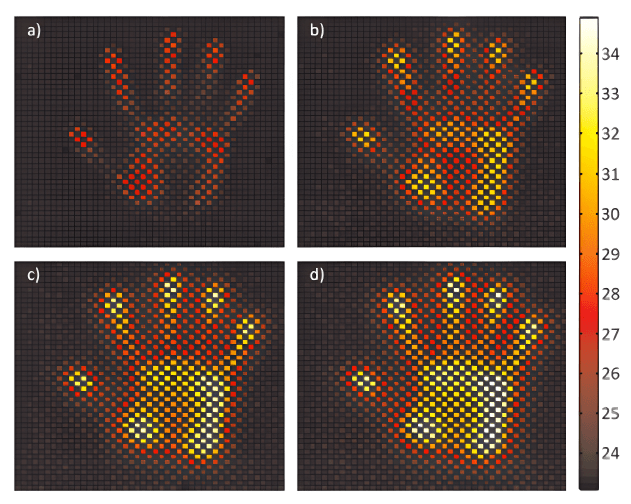
Source: http://zbum.ia.pw.edu.pl/PAPERS/ICB_2013_Czajka_Bulwan.pdf
Advantages
Provides a strong indicator of liveness.
Harder to spoof compared to optical methods.
Limitations
Can be affected by the ambient temperature.
May not work well with materials that retain heat.
4. Ultrasonic Liveness Detection
Ultrasonic scanners are considered to be more secure than optical and capacitive scanners. Standard ultrasonic methods use a transmitter, which releases high-frequency acoustic signals towards the fingerprint. A receiver detects the echo signals affected by the interaction from the fingerprint. It is important to note that the receiver utilizes the fact that the skin(ridges to be specific) and the air (valleys) have differences in the sound wave interference, making the echo signals reflect and diffract differently in the contract area. Keep in mind that this approach with liveness testing capabilities among its principles utilizes the fact that sound waves are not just reflected and diffracted, they are also subject to some additional scattering & transformation.
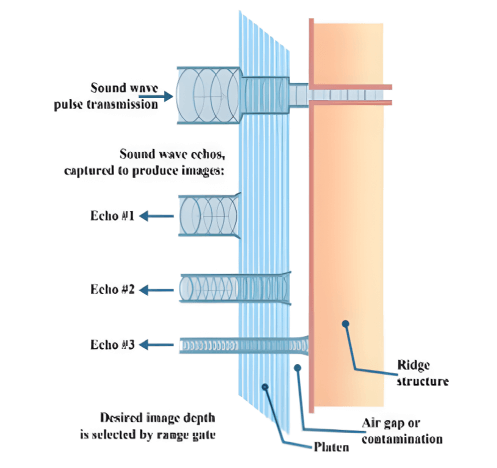
Source: https://www.google.co.in/books/edition/_/T3WfDwAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1
Advantages
High accuracy in detecting liveness
Capable of reading through the dirt, moisture, and other contaminants
Limitations
More expensive and complex to implement
May require more power, and face limitations to use in portable devices.
5. Multispectral Imaging
Multispectral imaging captures fingerprint images using various wavelengths of light, including visible and infrared. This technique allows for the analysis of both surface and subsurface features, making it possible to detect liveness by distinguishing genuine fingerprints from fake ones. By examining the fingerprint's layers in detail, multispectral imaging enhances security and accuracy in biometric systems, ensuring that the fingerprint being scanned is from a living individual and not a replica or spoof.
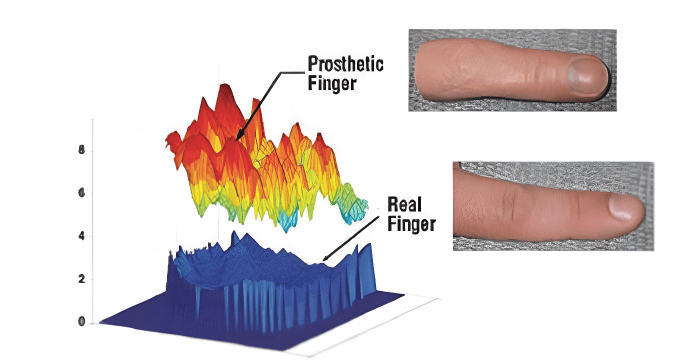
Source: https://www.google.co.in/books/edition/_/T3WfDwAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1
Advantages
Highly efficient in differentiating between real and fake fingerprints
Works well across different skin tones and conditions.
Limitations
Complex & costly technology
Can be slower than other technology as it needs more scans
Choosing the right liveness detection method is essential, you have to keep in mind that the method you’re planning to use should cover your every requirement. Remember that each of these methods has its strengths and benefits. To ensure optimal security, relying on a single technique isn't enough. It is recommended to combine multiple methods and provide a more effective layer of security against fingerprint spoofing.
The Future of Fake Fingerprint Detection
As the technology advances, the fingerprint spoofing methods will also need to evolve. Here are the key trends that you need to watch out for :
AI & Machine Learning
It will be easier to detect the fingerprint spoofing attempts with the help of AI and ML with advanced accuracy and speed along with the advanced data analysis.
Everyday Integration
As fingerprints are now part of our daily lives, it will be vital to have more affordable and effective detection methods for devices that we use every day such as smartphones and smart home systems.
Multimodal Biometrics
It is always recommended to rely on more than one biometric for an extra layer of protection. You can combine various authentication methods such as an iris scanner with a fingerprint scanner for strengthening security.
Ongoing Innovations
Last but not the least, is the ongoing innovations. Continuous advancements are necessary to stay ahead of evolving fingerprint spoofing techniques. By developing and refining detection methods, we can outpace new threats and ensure robust security against the rapidly increasing sophisticated fingerprint spoofing attack.
Conclusion
The threat of fingerprint spoofing is a growing concern for biometric security. It is essential to understand the nature of these threats and the various detection methods available for securing the sensitive information and preventing any unauthorized access. By continually improving detection technologies & employing a multi-layered approach, we can enhance the security of fingerprint recognition systems and protect against the risks associated with spoofing. As technology evolves, so must our strategies for ensuring the integrity of biometric systems, making ongoing research and development a priority for the future.